MS treatment - latest development

The immune response of the body is a complex multicomponent reaction of the immune system, which occurs in response to a foreign antigen, i.e. to the pathogenic protein of cells from pathogenic bacteria, viruses and fungi. Once in the body, antigens cause the activation and fast proliferation of immune cells: T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes, which recognize antigens and kill pathogenic organisms. In that way, the body gets rid of the infection. After suppressing the pathogenic cells, the activated T and B lymphocytes can harm the organism and therefore they are deactivated (suppressed) by other immune system cells, the regufonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans%7CBaumans%7CLato%7COswald:600ry T-cells (Treg). In the case of healthy people, the number of Tregs oscillates between 5.6 and 8.6% of the total number of T-lymphocytes, i.e. 57 - 98 cells per 1 ml of blood.
The pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases is based on the activation of T-lymphocytes by the antigens of own non-pathogenic cells from various tissues. T-lymphocytes attack normal tissue, causing injuries thereto: In the case of multiple autoimmune sclerosis, the central nervous system is affected by an autoimmune effect; in the case of lateral amyotrophic syndrome, motor neurons are affected; in the case of autoimmune arthritis, the chondrocytes and the articulation sheath are affected; in the case of systemic lupus erythematosus, the connective tissue and the vessels are affected etc. Patients with autoimmune diseases display a significant decrease in the quantity of Tregs in the blood and/or a failure of their suppressive function. The decrease in the number of Tregs in the blood is correlated with the severity of the autoimmune disease, while the reduction rate is correlated with the expected time for the adverse outcome.
At our clinic we have introduced the latest method of treating autoimmune diseases by means of autologous cultured exvivo Treg cells. The term "autologous" refers to a transplantation, in which the transplantation tissue is taken from the recipient himself. Exvivo cultivation means "something that happens outside the body," i.e., the growth of living cells, transferred from the organism into an artificial external environment. In this way, the patient receives his own Treg cells, which have been artificially reproduced outside the organism. The level of Tregs in the patient's blood reaches the level of a healthy person, which is accompanied by the suppression of autoaggressive immune cells and the mitigation or complete disappearance of autoimmune symptoms.
For the successful treatment of Treg cells, the patient must go through several mandatory steps.
The first step consists in taking no more than 1 ml of venous blood from the patient. This sample is submitted to a Treg quantity analysis by the method of flow cytometry. Based on these results, the attending physician will decide whether the patient should undergo the treatment with cultivated Treg cells.
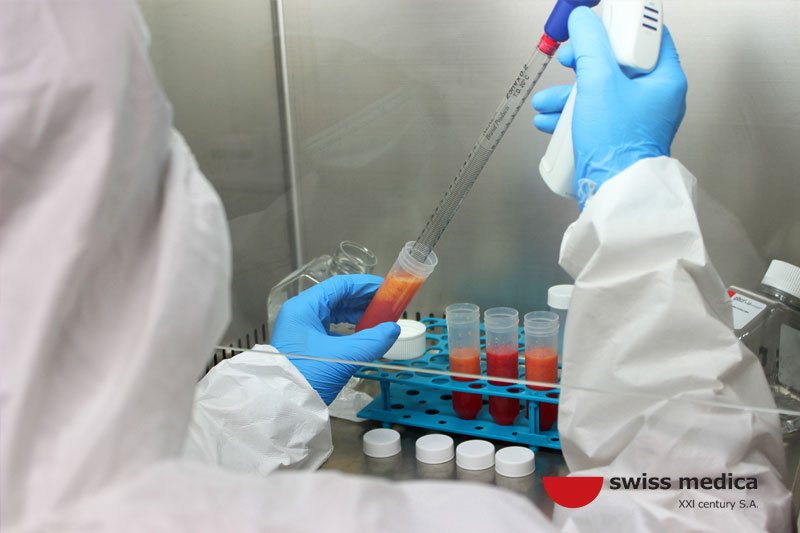
In the second phase, 70-80 ml of blood are taken from the patient and used to release and cultivate exvivo Treg cells during 6-7 days. The number of Treg cells in culture conditions increases hundreds of times.
In the third stage, the mature cultured Treg cells are administered back to the patient.
Two weeks later a new analysis is carried out to determine the number of Treg cells in the blood.
The main objective of the Treg cell therapy is to bring the quantity of these cells in the patient's blood to the level of healthy people. Our experience shows that it is necessary to perform 2-5 Treg cell administration procedures in order to achieve a "healthy" level, which will be later on maintained by means of 3-4 administration procedures per year. The number of administration procedures depends on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. It will be defined by the attending physician based on the Treg cell quantity analysis.
The main advantage of the Treg cell therapy technology for the treatment autoimmune diseases consists in the immediate effect on the pathogenesis of the disease, i.e. in the correction of the regufonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans%7CBaumans%7CLato%7COswald:600ry processes of the immune system. This technology is extremely safe, because it uses autologous cells, i.e. the donor's cells. No cases of rejection of the cells or inflammation at the administration site have been observed. No adverse reactions or undesirable events have been observed as a result of this method of therapy.
Another advantage of this therapy method is the possibility of combining it with conventional symptomatic treatments.
As an example, we will illustrate the treatment of two patients with autoimmune diseases.